What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Common Symptoms
FEET PAIN
- Feet/toe pain
- Tingling, prickling, or numbness in feet
- Sharp, stabbing, throbbing, burning pains
- Muscle weakness
- Sensitivity to touch
- Heavy feeling sensation
- Difficulty walking
- Lack of coordination

HAND PAIN
- Hand/forearm pain
- Tingling, prickling, or numbness in hands
- Sharp, stabbing, throbbing, burning pains
- Muscle weakness
- Dropping of items
- Feels like wearing a glove
- Sensations of shocking or buzzing

FEET PAIN
- Feet/toe pain
- Tingling, prickling, or numbness in feet
- Sharp, stabbing, throbbing, burning pains
- Muscle weakness
- Sensitivity to touch
- Heavy feeling sensation
- Difficulty walking
- Lack of coordination

HAND PAIN
- Hand/forearm pain
- Tingling, prickling, or numbness in hands
- Sharp, stabbing, throbbing, burning pains
- Muscle weakness
- Dropping of items
- Feels like wearing a glove
- Sensations of shocking or buzzing

Learn more about peripheral neuropathy and how it can affect other areas of your body.
Peripheral Neuropathy
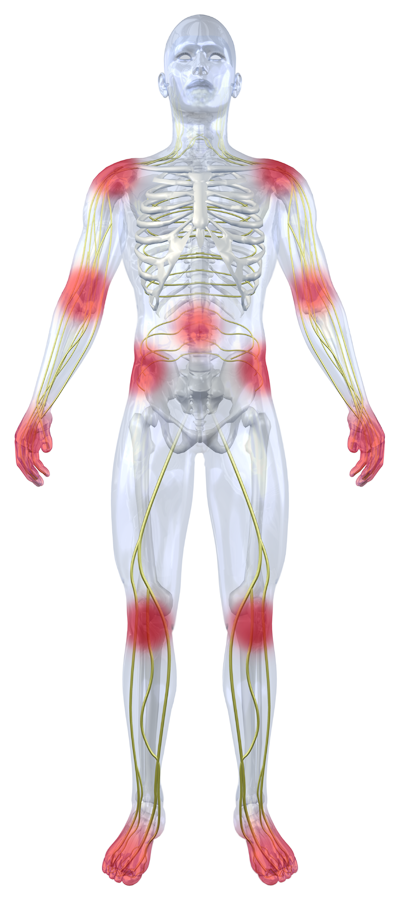
Peripheral Neuropathy is the damage of the nerves surrounding the outside of the brain and spinal cord, or central nervous system. Sensory messages from the nerves are sent to and from the central nervous system, causing the affected areas to be in pain. Because every nerve in the peripheral system is designed to have a specific function, how the nerve is affected determines the system a person may experience.
Nerves are classified into sensory, motor and autonomic:
- Sensory nerves: receive sensation, such as temperature, pain, vibration or touch, from the skin
- Motor nerves: control muscle movement
- Autonomic nerves: control functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, digestion and bladder
Signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy might include:
- Tingling, prickling, or numbness in hands, feet, or affected areas
- Sharp, stabbing, throbbing, burning pains in hands, feet, or affected areas
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Lack of coordination and balance
- Difficulty walking
- Muscle weakness
- Feels like wearing a glove
- Heavy feeling sensation
- Sensations of shocking or buzzing
Most people with peripheral neuropathy have polyneuropathy, meaning multiple nerves.
Peripheral Neuropathy is nerve damage caused by a number of conditions that may include:
- Autoimmune diseases: Sjogren's syndrome, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, vasculitis, and chronic. inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy.
- Diabetes: Over half the population with diabetes develop some type of neuropathy.
- Infections: Certain viral or bacterial infections such as Lyme disease, shingles, Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, hepatitis B and C, leprosy, and diphtheria.
- Inherited disorders: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a hereditary type of neuropathy.
- Tumors: Growths, either cancerous and noncancerous, can develop on the nerves or press nerves.
- Bone marrow disorders:Abnormal protein in the blood, certain forms of bone cancer, and a lymphoma.
- Other diseases: Kidney and liver disease, connective tissue disorders, or hypothyroidism.
- Alcoholism:Poor dietary choices lead to vitamin deficiencies in alcoholics.
- Exposure to poisons: Toxic substances such as lead and mercury.
- Medications: Certain medications, namely those used to treat cancer with chemotherapy, can cause peripheral neuropathy.
- Vitamin deficiencies:Crucial vitamins include Vitamin B-1, B-6 and B-12, Vitamin E and niacin.
- Trauma or pressure on nerve: Accidents, injuries, infections or extended pressure on a nerve.
Peripheral neuropathy risk factors may include:
- Diabetes
- Alcoholism and abuse
- Vitamin deficiencies (B Vitamins, Vitamin E, and niacin)
- Infections, such as Lyme disease, shingles, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis B and C, and HIV
- Autoimmune diseases
- Kidney, liver or thyroid disorders
- Exposure to toxins
- Repetitive motions
- Family history of neuropathy
Complications of peripheral neuropathy can include:
- Burns and skin trauma if numbness restriction sensation to feel pain.
- Infection due to lack of sensation leading to unknow injury.
- Falls from weakness, difficultly with coordination, balance problems, and loss of sensation.
Identify and manage underlying conditions
Identification and management of underlying conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases, kidney and liver disease, thyroid disorders, vitamin deficiencies, alcoholism, and exposure to toxins need to be addressed. While it is important enroll a medical professional to accurately diagnose medical conditions, it’s also important for patients to educated themselves on prevention measures.
Healthy lifestyle choices to support nerve health:
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean protein to keep nerves healthy or as advised by a medical professional.
- Exercise regularly as advised by a medical professional.
- Avoid factors that may cause nerve damage.
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen and NSAIDS, can help treat mild-to-moderate pain associated with peripheral neuropathy.
Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen can be used to treat mild-to-moderate pain, reduce fevers and can provide relief by reducing the amount of pain one can tolerate before experiencing pain. Acetaminophen it is not very effective at reducing inflammation. The best-known brand of acetaminophen is Tylenol®, but other generic drugs can be purchased over the counter.
NSAIDS - Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NSAIDS, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are designed to reduce pain, swelling, stiffness and inflammation. NSAIDS work by reducing the body’s production of prostaglandin, an enzyme that sends pain messages to the brain. When taken regularly, they build up in the blood to levels that fight pain caused by inflammation and swelling.
Most common types of NSAIDS are:
- Aspirin (Bayer® Aspirin, Ecotrin®, Excedrin®)
- Ibuprofen (Advil®, Motrin®)
- Ketoprofen (Orudis®)
- Naproxen (Aleve®)
Other brands of generic NSAIDS can be purchased over the counter.
Topical active drug medications in the form of creams, ointments, gels, lotions or patches can be applied directly on the skin. The medications provide relief from nerve pain and inflammation by absorbing though the skin and treat the localized area. Medications to treat neuropathy pain are analgesics and local anesthetics.
- Analgesics: Nonprescription topical pain relievers used to provide temporary relief and are delivered on the skin’s surface. These medications contain capsaicin (Capzasin-P®, Dolorac®, Zostrix® are brand names).
- Local anesthetics: Used to treat localized pain by numbing the area and blocking the pain signal.
Transcutaneous electronic nerve stimulation (TENS) is a drug-free method of therapy that may be used to treat acute nerve pain by inhibiting pain signals from reaching the brain. Very small electrical impulses on specific nerve path are delivered through electrodes place on the skin’s surface. TENS may be prescribed by a medical professional in combination with other treatments.
Patient’s suffering with peripheral neuropathy may be prescribed medication by a medical professional.
Sometimes, drugs developed and used to control other conditions are effective pain relievers. In addition to relieving depression, many anti-depressant drugs can relieve chronic pain. These drugs also may improve sleep quality, which may in turn help reduce pain. In some cases, antidepressants work by treating accompanying depression that makes chronic pain more difficult to handle.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) (e.g., Cymbalta®)
- Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (e.g., Wellbutrin®)
- Serotonin Receptor Modulators (SRM)
Patients often seek drug-free, complementary and alternative therapies help manage pain caused by peripheral neuropathy. They may be used alone or may be combined with other medications and treatments. The goal is to combine a non-invasive approach to also help the body heal, including prevention awareness.
Commonly used therapies are advertised by wellness provider, holistic centers, medical practices and independent practitioners. Many popular therapies include and are not limited to:
- Acupuncture:
- Laser therapy:
- Biofeedback:
- Ergonomics and Splints:
- Relaxation techniques:
- Cold therapy:
